Hải Đăng PPK gửi vào
- 45813 lượt xem
I. CHUẨN BỊ
Hầu hết các module micro đều làm việc miễn là được cắm vào cổng analog của arduino của bạn.
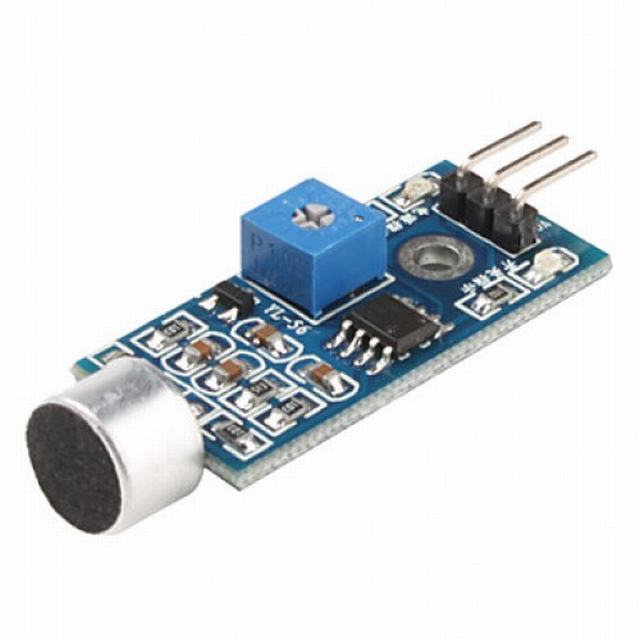

II. TRƯỚC KHI BẮT ĐẦU
Để arduino có thể nhận dạng được giọng nói chúng ta cần sử dụng thư viện μSpeech (mirror)
Thư viện μSpeech cung cấp một chức năng nhận dạng giọng nói bằng cách sử dụng Arduino. Nó xác định âm thanh bằng cách phân tính tần số âm vị. Và như vậy nó không có cách nào để phân loại các giọng đọc khác nhau của 1 từ . Và việc đó cần đến người sử dụng thiết lập, dẫn đến khó khăn cho nhiều người trong việc muốn tiếp cận đến thư viện
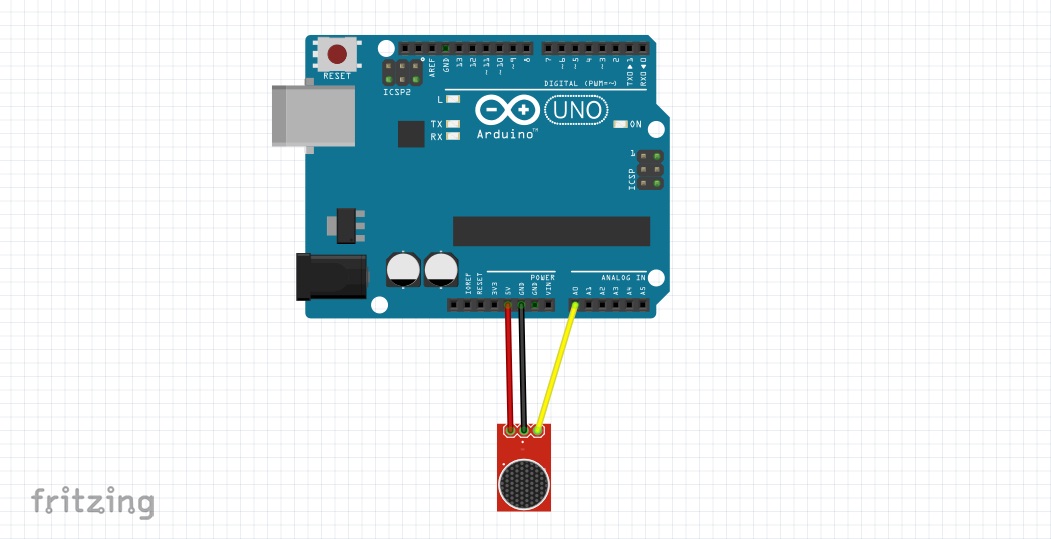
Thực sự mà nói thì thư viện này hỗ trợ rất tốt trong việc xác định các từ s,z,f (Phát âm theo tiếng anh) Bởi vì nó được tạo bởi người sử dụng tiếng anh, nó ứng dụng trong các câu lệnh như Stop, right, left, tuy nhiên các bạn cũng có thể thử với ngôn ngữ tiếng việt.
III. CODE
Sau khi các bạn đã down thư viện về, copy vào thư mục library của arduino và tiến hành cài đặt lại âm vị cho thư viện bằng cách sử dụng đoạn code sau
#include <uspeech.h>
signal voice(A0);
char option = 0;
uint32_t power(uint32_t base, uint32_t exp);
void setup()
{
#if 0
int minVolume; /*!< Mức âm thanh tối thiểu mà bạn cho là nó sẵn sàng có thể thu được âm */
int fconstant; /*!< cài ngưỡng cho âm /f/ */
int econstant; /*!< cài ngưỡng cho âm /ee/, /i/, */
int aconstant; /*!< cài ngưỡng cho âm /a/ /o/ /r/ /l/, */
int vconstant; /*!< cài ngưỡng cho âm /z/ /v/ /w/, */
int shconstant; /*!< cài ngưỡng cho âm /sh/ /ch/, /s/ */
bool f_enabled; /*!<thiết lập này để ở false nếu bạn không muốn xác định âm /f/s */
int amplificationFactor; /*!<Amplification factor: điều chỉnh khi cần*/
#endif
analogReference(EXTERNAL);
voice.f_enabled = true;
voice.fconstant = 240;
voice.econstant = 2; //3; //1 2;
voice.aconstant = 4; //5; //2 4;
voice.vconstant = 6; //7; //3 6;
voice.shconstant = 8; //4;
voice.amplificationFactor = 10;
voice.micPowerThreshold = 80;
voice.scale = 8;
Serial.begin(115200);
#if 0
while (1) {
uint16_t sig = analogRead(A0);
Serial.println(sig);
delay(100);
}
#endif
Serial.println(F("Calibrating"));
voice.calibrate();
Serial.print(F("Calibrated at "));
Serial.println(voice.calib);
Serial.println(F("Ready"));
}
uint16_t lastMicPower=0;
char lastPhoneme = ' ';;
uint16_t lastCoeff=0;
uint16_t lastPower=0;
uint32_t lastChange = 0;
uint32_t startUsec = 0;
uint8_t col=0;
char buf[80];
struct history_s {
int micPower;
int coeff;
char phoneme;
char f_phoneme;
uint32_t usecs;
} history[80];
uint32_t power(uint32_t base, uint32_t ex)
{
if (ex == 0)
return 1;
else if (ex % 2)
return base * power(base, ex - 1);
else {
int temp = power(base, ex / 2);
return temp * temp;
}
}
void pad(uint32_t value, uint8_t places)
{
uint32_t padValue = power(10, places);
while (value < padValue) {
Serial.print(' ');
padValue /= 10;
}
Serial.print(value);
}
void loop()
{
char phoneme = voice.getPhoneme();
if (option==0) {
Serial.println(F("uSpeech debug tool--------"));
Serial.println(F(" nhan 'f' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra thong so f"));
Serial.println(F(" nhan 'p' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra getPhoneme"));
Serial.println(F(" nhan 'v' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra volume of your microphone"));
Serial.println(F(" nhan 'c' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra coeff"));
option = 1;
}
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
option = Serial.read();
}
switch (option) {
case 'f': {
uint16_t micPower = voice.micPower;
if (micPower != lastMicPower) {
Serial.print(F("micPower: "));
Serial.println(micPower);
lastMicPower = micPower;
}
}
break;
case 'p': {
if (phoneme != lastPhoneme || phoneme != ' ') {
if (col == 0) {
startUsec = micros();
}
lastPhoneme = phoneme;
buf[col] = phoneme;
history[col].phoneme = phoneme;
history[col].f_phoneme = voice.phoneme;
history[col].coeff = voice.testCoeff;
history[col].micPower = voice.micPower;
history[col].usecs = micros() - startUsec;
startUsec = micros();
if (++col >= sizeof(buf)-1) {
buf[col] = 0;
Serial.println(F("phonemes"));
for (uint8_t ind=0; ind<col; ind++) {
Serial.print(F(" "));
pad(history[ind].usecs,5);
Serial.print(F(": '"));
Serial.print(history[ind].phoneme);
Serial.print('\'');
Serial.print(F(" ("));
Serial.print(history[ind].coeff);
Serial.print(',');
Serial.print(history[ind].micPower);
Serial.println(')');
}
Serial.print(F("phoneme sequence: \""));
Serial.print(buf);
Serial.println('"');
col = 0;
}
lastChange = millis();
}
if (col && ((millis() - lastChange) > 50)) {
buf[col] = 0;
Serial.println(F("phonemes"));
for (uint8_t ind=0; ind<col; ind++) {
Serial.print(F(" "));
pad(history[ind].usecs,5);
//Serial.print(history[ind].usecs);
Serial.print(F(": '"));
Serial.print(history[ind].phoneme);
Serial.print('\'');
Serial.print(F(" ("));
Serial.print(history[ind].coeff);
Serial.print(',');
Serial.print(history[ind].micPower);
Serial.print(')');
if (history[ind].phoneme == 'f') {
Serial.print(" '");
Serial.print(history[ind].f_phoneme);
Serial.println('\'');
} else {
Serial.println();
}
}
col = 0;
Serial.print(F("phoneme sequence: \""));
Serial.print(buf);
Serial.println('"');
Serial.println(F("-----------------------------"));
}
}
break;
case 'v': {
uint16_t power = voice.power();
if (power != lastPower) {
Serial.print(F("power:"));
Serial.println(power);
lastPower = power;
}
}
break;
case 'c': {
uint16_t coeff = voice.testCoeff;
if (coeff != lastCoeff) {
Serial.print(F("coeff: "));
Serial.println(coeff);
lastCoeff = coeff;
}
}
break;
case 1:
break;
default:
option = 0;
if (col) {
Serial.println();
col = 0;
}
break;
}
}
Đoạn code trên bạn có thể tìm thấy trong mục example của library vừa down về.
Sau khi nạp code xong, các bạn mở serial monitor lên sẽ thấy hiển thị đoạn sau:
uSpeech debug tool-------- nhan 'f' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra thong so f nhan 'p' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra getPhoneme nhan 'v' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra volume of your microphone nhan 'c' neu ban muon hieu chinh/kiem tra coeff
Bạn hãy nhấn từng lựa chọn, ví dụ: nhấn f + enter, sau đó bạn hãy nói âm f vào micro(nói bằng tiếng anh nhé, âm đuôi, dạng như phừ phừ) màn hình sẽ hiển thị lên 1 loạt thông số, bạn chọn thông số chung nhất và ghi lại. mình lấy ví dụ thông số cho âm f là 380. Tương tự như vậy đối với các âm /ee/; /i/; /o/; /z/;/sh/.... mà ở phần khai báo trong void setup() đã chú thích rõ. Sau khi đã có đủ các thông số, chúng ta sẽ cùng đến ví dụ đầu tiên.
Bật tắt led
#include <uspeech.h>
#define led 13
signal voice(A0);
String collvoice;
char prev;
boolean newline=false;
int sum = 0;
void setup(){
voice.f_enabled = true;
voice.minVolume = 1500;
voice.fconstant = 380;
voice.econstant = 1;
voice.aconstant = 2;
voice.vconstant = 3;
voice.shconstant = 4;
voice.calibrate();
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
void loop(){
voice.sample();
char p = voice.getPhoneme();
if(p!=' '){ // nếu có âm thanh
if((p=='f')){ // nếu âm thanh nhận được là f
newline = true;
}
else{
newline = false;
}
}
else{
if(newline){
digitalWrite(led, LOW);
}
else{
digitalWrite(led, HIGH);
}
}
}Như các bạn thấy, thông số 380 được đưa vào khai báo ban đầu cho âm vị f. các âm vị khác cũng làm tương tự. khi nạp code. Như các bạn biết, tiếng anh tắt nghĩa là OFF và đọc là "óp phừ"  và khi các bạn đọc off, đèn sẽ tắt.
và khi các bạn đọc off, đèn sẽ tắt.
Tuy nhiên các bạn có thể sử dụng tiếng việt.nó sẽ không thể phần biệt được từ có và cỏ. Nhưng nó có thể phân biệt được giữa có và không, bật và tắt, trái và phải. Hãy cùng thử xem nhé.
Chúc các bạn thành công!



 Qua bài viết này, hi vọng nhận được nhiều ý kiến đóng góp từ các bạn đồng thời nâng cấp thêm nhiều tính năng cho thiết bị.
Qua bài viết này, hi vọng nhận được nhiều ý kiến đóng góp từ các bạn đồng thời nâng cấp thêm nhiều tính năng cho thiết bị.

